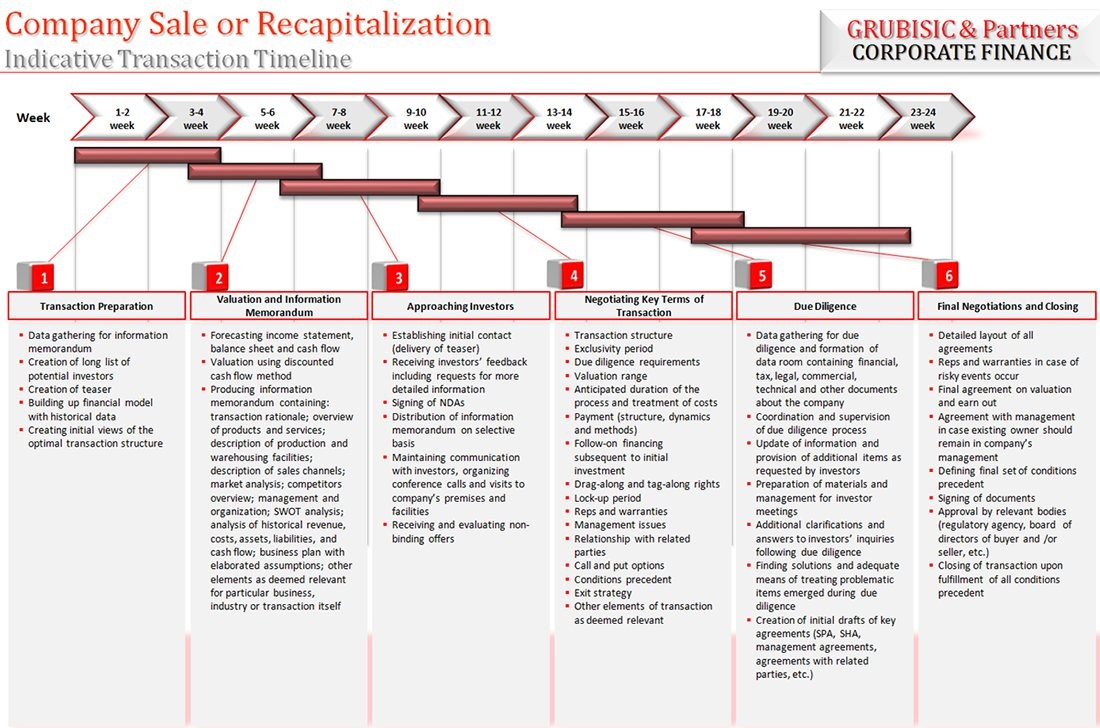
Company Sale or Recapitalization by Strategic or Financial Investor
Transaction Planning, Preparation of Information Memorandum and List of Potential Investors
Transaction Preparation
- Meetings with management and agreement on indicative transaction timeline
- Defining transaction structure
- Creating list of potential investors
- Preparing initial transaction documents for investors
- Teaser
- Non-Disclosure Agreement (NDA)
- Estimate of valuation range
Preparation of Information Memorandum
- Information Memorandum is a document with detailed information about the company and envisaged transaction, which includes among other things:
- Overview of the market (size, trends, potential growth), market shares, description of competitors, barriers to market entry of new competitors, etc.
- Overview of products and services, manufacturing sites and facilities, sales and distribution channels, customer structure, etc.
- Management and SWOT analysis
- Key investment highlights (why it makes sense to acquire ownership in the company)
- Historical financial statements, analysis of revenue, expenses, assets and liabilities
- Business plan and financial projections
- Other data, information and analysis relevant to the transaction
Initial Contact and Continued Communication with Potential Investors
- Establishing of initial contact with investors (by sending teaser)
- Signing of confidentiality agreement upon receiving feedback and request for additional information
- Distribution of information memorandum to interested investors
- Maintaining constant communication with investors and responding to inquiries
- Organizing meeting and conference calls with company’s management
- Updating information memorandum as needed
Negotiating Key Terms and Conditions of Transaction (Term Sheet) and Preparation for Due Diligence
Negotiating Term Sheet
- Non-binding offers come in the form of Memorandum of Understanding, Letters of Intent or Term Sheet, before the start of due diligence, which depending on the type of investor and type of transaction usually includes:
- Transaction structure
- Period of exclusivity in negotiating and executing due diligence
- Valuation range and assumptions upon which it is determined
- Anticipated duration of the process and treatment of costs incurred during the process
- Structure, dynamics and form of payment (cash, shares, assets, retained part of the purchase price for warranties, earn out, etc.)
- Representations and warranties to be provided by seller (or vice versa)
- Requirements for additional funding (capital increase) in the period after the entry of investor
- Lock-up period
- Treatment of business relationships between the company and related parties
- Conditions precedent for closing
- The basic outline of the Shareholders' Agreement
- Buyer and seller representation in management and supervisory board
- Exit strategy for the founder and/or investor (initial public offering on the stock market, selling to a strategic buyer or financial investor, etc.)
- Other elements of the non-binding offer that are essential for the implementation of the specific transaction
Organizing and Following Execution of Due Diligence
- Organization and coordination of due diligence performed by investors including:
- Collecting documentation for due diligence
- Preparation of data room in which the potential buyer as part of due diligence will have access to relevant legal, technical, commercial and financial documents
- Coordinating and monitoring the process of due diligence
- Preparation of materials and management for meetings with interested investors during due diligence
- Answering additional questions and distribution of additional documents to interested investors at the end of due diligence
Representations and Warranties, Treatment of Problematic Items From Due Diligence, Final Valuation, SPA and SHA
Final negotiations and Transaction Agreements
- Consulting in final negotiations usually includes:
- Advising on Share purchase agreement (SPA)
- Advising on Shareholder agreement (SHA)
- Defining final set of seller’s representations and warranties
- Treatment of certain items arising from due diligence
- Negotiating final valuation and earn out (if any)
- Advising on contracts with management in case existing owners who are at the same time managers remain in the ownership structure
- Other elements essential for transaction closing